The children seem like typical kindergartners: Some beam at the camera; some glance coyly aside; others appear lost in reverie. One slim, dark-haired girl in a pale dress looks precociously serious.
She is Anne Frank, and this classroom photograph, taken at a Montessori school in Amsterdam in 1935, appears twice in “Anne Frank the Exhibition,” a 7,500-square-foot multimedia installation that opens on Monday — International Holocaust Remembrance Day — for a three-month stay at the Center for Jewish History in New York before traveling to other cities.
Visitors first see the picture in one of the exhibition’s introductory rooms, before they walk through the show’s core: the first full-scale re-creation of the secret annex that was the Amsterdam hiding place of eight Jews, including the Frank family, from July 1942 to August 1944. In those cramped, cloistered spaces, Anne wrote her famous diary.
When viewers encounter the kindergarten photograph again, this time as an animation, it delivers a gutting blow: As an audio track reveals their names, their ages at death and the places where they were killed, 10 of the classroom’s Jewish children, one by one, turn into black silhouettes and disappear from the picture, their images erased as swiftly and summarily as the Nazis ended their lives.
Appearing after the annex, this animation introduces “a very personal, intimate, heartbreaking element of schoolchildren who were murdered for no other reason than the fact that they were Jewish,” said Ronald Leopold, executive director of the Anne Frank House in Amsterdam, as he walked amid cables and boxes during the New York show’s construction.
Created by the Anne Frank House and presented in partnership with the Center for Jewish History, the entire installation aims to examine Anne Frank’s life — and death — with a scope not often found in other treatments of this chapter in history. And while Leopold said the current political climate did not inspire the exhibition, it opens when antisemitism is rising in the United States and abroad, and when American popular culture has been turning to visual mediums to resurrect the memory of the Holocaust: fact-inspired dramas like the television mini-series “We Were the Lucky Ones” and the movie “The Survivor” and award-winning recent fictional films like “The Brutalist” and “A Real Pain.”
“Anne Frank the Exhibition” is the answer of the Anne Frank House to “how this history, how this memory will go into the 21st century,” Leopold said.
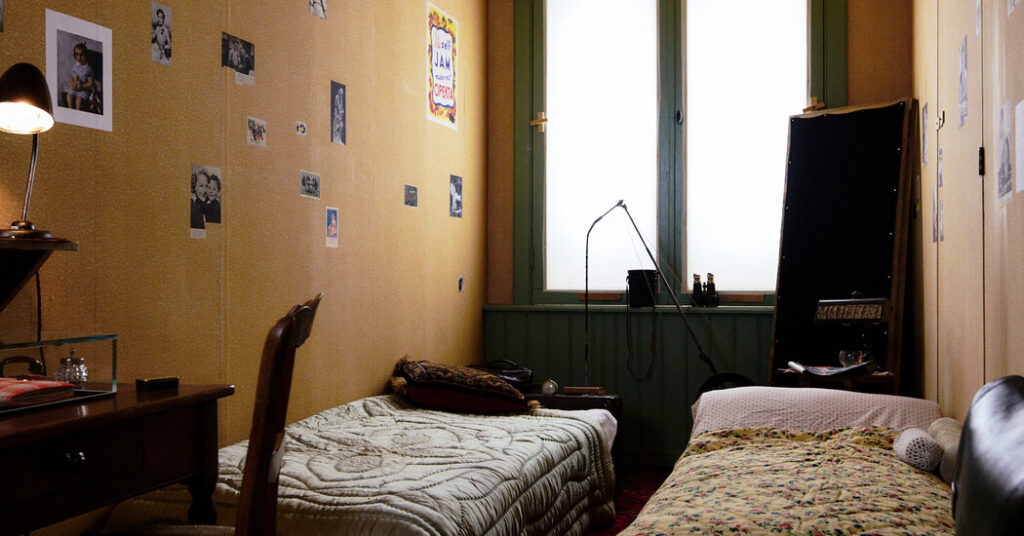
Following a chronological path, the installation traces Anne and her family from the 1920s in Frankfurt, Germany, through their flight to Amsterdam. It is only after exploring this early history that visitors encounter the reconstructed annex: five shadowy rooms whose exact dimensions and details the exhibition team has copied from their original location in the Anne Frank House in Amsterdam, down to the covered windows and bits of peeling wallpaper.
The show goes on to chronicle the return from Auschwitz of Otto Frank, Anne’s father and the sole survivor among the eight hidden Jews. Visitors discover how Otto learned the fates of his wife and two daughters and how he pursued the publication of Anne’s diary: 79 editions in different languages are on display, along with memorabilia from the theatrical and film adaptations. He also secured the preservation of the annex in Amsterdam, now a museum space that admits some 1.2 million visitors annually.
“We all know that the diary is about the two years in hiding,” Tom Brink, the head of collections and presentations at the Amsterdam house and the traveling exhibition’s curator, said in an interview. “But of course, the story is much bigger than that. It starts earlier, it ends later, and that entire story and entire journey deserves to be told.”
Working with Eric Goossens, the exhibition’s designer, Brink confronted the challenge of relating that history more than 3,600 miles away from the real annex, tucked into the back of the canal-side house where Otto Frank ran his business. In Amsterdam, the annex is completely empty except for some material on the walls, including Anne’s pictures of movie stars and artworks.
Otto Frank requested that the spaces, plundered by the Nazis, remain vacant, their barrenness attesting to profound loss. But using his and others’ accounts, the New York exhibition’s team has filled each annex room with furniture and possessions, including books and a board game retrieved from the original space.
“Otherwise, it would just be four walls,” Brink said. “In Amsterdam, it’s just four walls, but it’s more than just four walls. It’s the fact that you’re in the actual place. That is not the case here.”
The re-creation, however, may lead to controversy. The novelist and essayist Dara Horn, for instance, has asserted that any Anne Frank exhibition inevitably cheapens and commercializes the girl’s memory, turning her into a symbol of easy uplift.
Agnes Mueller, a professor and a fellow in Jewish Studies at the University of South Carolina and a fellow at the American Academy in Berlin, has similar concerns. “My instinct says that when Otto Frank wanted the annex to be empty in the original Anne Frank House in Amsterdam, he was worried about that kind of commercialization and universalization of the persona of Anne Frank, and so he actually emphasized absence as a way to represent that which is not representable,” she said in a video interview. The sight of an annex room filled with homey touches, she added, “might induce us to feel way too good about things that we should not feel good about.”
Many items in the recreated annex, however, are wrenching, as they reveal its occupants’ expectations for an unrealized future. Anne Frank, 13 when she went into hiding, took her diary — a facsimile is here; the original remains in Amsterdam — and Peter van Pels, the teenage boy who briefly won her heart, took his cat (a model of the pet carrier is in the reconstructed spaces) and his bicycle (also a reproduction). In his parents’ room, his mother, Auguste, hung a festive black dress, an original artifact never before displayed and now in the show.
Mueller acknowledged that an annex filled with artifacts would probably have far more impact on young viewers than empty spaces. Since the exhibition, which she has not seen, is intended to bring Holocaust history to future generations — more than 250 school tours have already been booked — it could lead “toward a better understanding of what the Holocaust might have been,” she said. (American knowledge of those events is poor; one 2020 survey of millennials and members of Generation Z revealed that almost half could not name a single concentration camp or Nazi-era Jewish ghetto.)
The show does not neglect the horror. Although a smiling photo of Anne is at the entrance, the exhibition’s audio guide — included with tickets — begins by giving away the story’s unhappy ending: The Nazis discovered the annex’s occupants and arrested them.
Containing more than 100 original artifacts, the installation features quotations from the Franks, along with objects from their personal histories: furniture, friendship albums, correspondence, a Torah. The display rooms chronicle the political climate of the 1920s and ’30s. A blown-up image of a 1938 Nazi rally appears repeatedly on the walls, its cheering participants teenage girls no older than Anne and her sister, Margot.
Another introductory room recreates the atmosphere of Amsterdam in 1940-42. On a continuous loop, a montage of film and photos covers the walls, interspersing scenes of family life with images including roundups of Jews, deportation trains and anti-Jewish regulations that “kept coming and kept coming,” Brink said.
The annex is behind a reproduction of the bookcase that covered its entry. After leaving the reconstructed hiding place, visitors walk onto an illuminated glass floor covering a full map of Europe, with the site of every death camp or mass killing of Jews marked by a small flag. One wall has an aerial view of Bergen-Belsen, where Anne and Margot died in February 1945 — only a few months before Germany surrendered; other panels display photographs of roundups, camp prisoners, Nazi shootings, the Warsaw ghetto. At the end of this gallery, the kindergarten photograph undergoes its repeated transformation.
“The immersive element in this exhibition is very much to bring people back in time and in place,” Leopold said, especially young visitors.
To draw that audience, the exhibition, a nonprofit venture whose revenues support the missions of its two presenting partners, offers $16 tickets for weekday visits by those under 18. Providing curriculum materials to classes, it also grants free admission not only to New York City public-school field trips, but also to those from schools nationwide receiving federal (Title 1) funding.
“The intention is 250,000 students moving through the exhibition,” said Michael S. Glickman, the founder of jMUSE, an arts and culture consulting group, and an adviser to the show. Through online resources, he added, “our expectation is that we will be able to support another half a million students in their classrooms.”
Public programs will also offer adults additional perspectives on Anne Frank, whether it’s “the debates about the play from 1955, or the film of ’59, or any number of other present-day political debates about her legacy,” said Gavriel Rosenfeld, president of the Center for Jewish History. The author Ruth Franklin (“The Many Lives of Anne Frank”) will be interviewed at the center on Tuesday evening, and the novelist Alice Hoffman (“When We Flew Away”) will appear on Feb. 9. The center will also host a film series. (An extension of the show in New York is being considered; more venues will be announced in the spring.)
The mission is to sustain the memory of those 10 kindergarten classmates and the 1.5 million other Jewish children whose lives the Holocaust erased. Leopold said he hoped the show would inspire engagement as well as reflection.
“If this exhibition is doing anything, it’s not just teaching history,” he said. “It is also teaching about ourselves.”
Anne Frank the Exhibition
Jan. 27-April 30, Center for Jewish History, 15 West 16th Street, Manhattan; 212-294-8301, annefrankexhibit.org.
Read the full article here