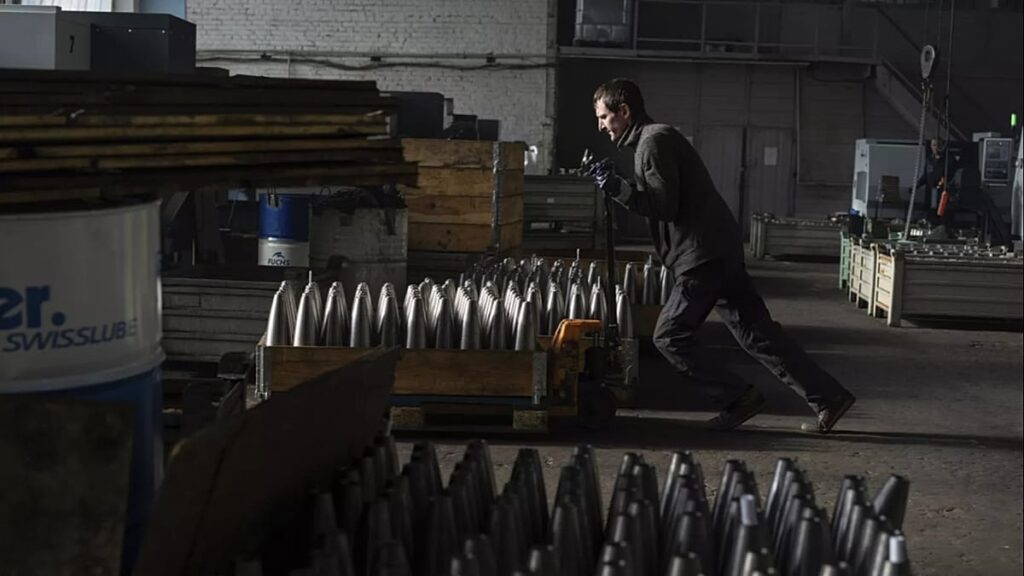
Arms sales by Italian companies to Ukraine have reached a total of just over €643 million since Russia launched its full-scale invasion in February 2022.
That’s a figure outlined in the Annual Report on Authorised Transit, Import and Export of Armaments which was submitted to parliament in spring. The document is a legal requirement, essential to ensure transparency on what for some is a particularly delicate economic activity.
According to the report, export authorisations to Ukraine grew significantly between 2022 and 2023, from just €3.8 million covering four authorisations to more than €417 million for 15 authorisations.
That value then dropped to just over €222 million in 2024 for just seven authorisations.
The report doesn’t specifiy which companies applied to export arms to Ukraine, nor is it known whether the transactions were actually carried out, although it is assumed that a large part of these sales actually went through.
Therefore, the report doesn’t help shine a light on which Italian manufacturers exported armaments to Ukraine.
However, it is known that the main players in the sector in Italy are RWM, Rehinmetall Italia and Leonardo. Euronews tried to contact Leonardo, asking if it was possible to find out if and what armaments had been sold to Ukraine, but there was no immediate answer.
Which kinda of weapons have been sold by Italian companies?
What is indicated in the report, however, is the type of armaments that have been exported.
In 2023, the €417 million of exports to Ukraine covered seven different categories: weapon systems above 12.7mm calibre, ammunition, fire direction equipment, land vehicles, toxic, chemical, biological, tear gas, radioactive materials, explosives and military fuels and finally electronic equipment.
As far as 2024 is concerned, the list is restricted to the first four categories.
However, these are not the only Italian arms that have reached Ukrainian territory. Those in the report to parliament are in fact only sales by Italian companies to Ukraine.
They do not, therefore, include military aid that has been granted as part of the aid packages prepared by the European Union, the next of which, the twelfth, is scheduled for early December.
‘Little transparency on the part of Italy’
“On this part, which is not covered by the report law 185/90, there has been little transparency on the part of Italy. Unlike what other European nations have decided,our country has in fact preferred not to provide any information about what has actually been supplied by our armed forces,” said Francesco Vignarca, spokesperson and activist of the Italian Network for Peace and Disarmament.
The information available is generally coming from the battlefield, based on what was actually seen at the Russian-Ukrainian front.
“It is difficult to estimate quantities and figures because many of these sales are secret,” said Eleaonora Tafuro Ambrosetti of the Ispi Institute for International Policy Studies.
“Between 2023 and 2024,” she adds, “Italy would have supplied Ukraine with Samp-T air defence batteries.”
Information kept secret so as not to give Russia an advantage
In comments to Euroenews, the press office of the Italian Defence Ministry confirmed that the “content” of Italian supplies as part of the packages to Kyiv is deliberately kept secret.
“Both Minister (Guido) Crosetto and his predecessor chose the same line, designed not to provide a technical advantage to Russia regarding what is on the battlefield. Only Copasir (the Parliamentary Committee for the Security of the Republic) is aware of this, but it too is required to maintain secrecy,” the ministry said.
It is even more difficult to quantify the value of what has been granted from the Italian armed forces’ arsenal.
“The mechanism envisaged by the European Union worked like this: each country that granted arms received a payment back from the EU itself, through the European Peace Facility fund. After a short time, however, it was clarified by Brussels that these funds would not be such as to allow the stocks to be replenished,” Francesco Vignarca of the Italian Network for Peace and Disarmament said.
This means that if a country sent more or less outdated equipment and vehicles to Ukraine and then wanted to buy new ones, it had to pay the difference between what it received from the EU and the purchase price.
This was stated by Defence Minister Guido Crosetto in a hearing before the joint Defence and Foreign Affairs Committees of the House and Senate. Even on this, however, no official figures were provided.
Italy contributed to the European Peace Facility
The Milex Observatory on Italian Military Expenditure indicated that “the only case ‘in the clear’ is that of artillery munitions.”
This accounts for €14.5 million that Article 33 of the Labour Decree of 2023 allocated to Agenzia Industrie Difesato “reinforce (munition) production to continue to respond to supplies to the Ukrainian armed forces without depleting national reserves.”
For the rest, as noted on several occasions by the Senate Budget Service and the Court of Auditors, there is little clarity as to how the disposals to Kyiv affect defence planning on the acquisition of armaments and related ammunitions.
Then there is the fact that Italy has granted €1.4 billion to the European Peace Facility**,** out of the total of €11.1 billion it has collected so far for Ukraine.
In the absence of precise data on how much the same fund has granted to Italy for the weapon systems it has sent, it is in short difficult to understand what the real cost of military support for Ukraine has been.
An estimate published in March 2023 by Milex, based on accessible sources, put the outlay for stockpile replenishment alone at around €1 billion.
Read the full article here