The United States military has moved nuclear weapons to British soil for the first time in close to two decades, new analysis indicates.
Open-source analysts identified an aircraft taking off from the Kirtland Air Force Base in Albuquerque, New Mexico, bound for the United Kingdom’s Royal Air Force (RAF) base at Lakenheath, in the east of England. Kirtland Air Force Base is the headquarters of the U.S. Air Force (USAF) Nuclear Weapons Center, a main storage site for nuclear weapons.
A U.S. defense official told Newsweek the U.S. did not comment on the “status or location of strategic weapons.” A spokesperson for the British Defense Ministry said: “It remains a long-standing UK and NATO policy to neither confirm nor deny the presence of nuclear weapons at a given location.”
Why It Matters
Speculation has long surrounded whether the East England RAF base could once again host U.S. nuclear weapons. RAF Lakenheath hosted American nuclear weapons for several decades until 2008.
The Federation of American Scientists (FAS) said in 2023 that U.S. military budget documents “strongly” implied the Air Force intended to re-establish its nuclear weapons mission in the U.K. RAF Lakenheath—the home of the 48th Fighter Wing, dubbed “Liberty Wing”—has been upgraded in recent years.
If Washington moves nuclear weapons back into the U.K., “it would break with decades of policy and planning and reverse the southern focus of the European nuclear deployment that emerged after the end of the Cold War,” the FAS said in updated analysis earlier this year.
What To Know
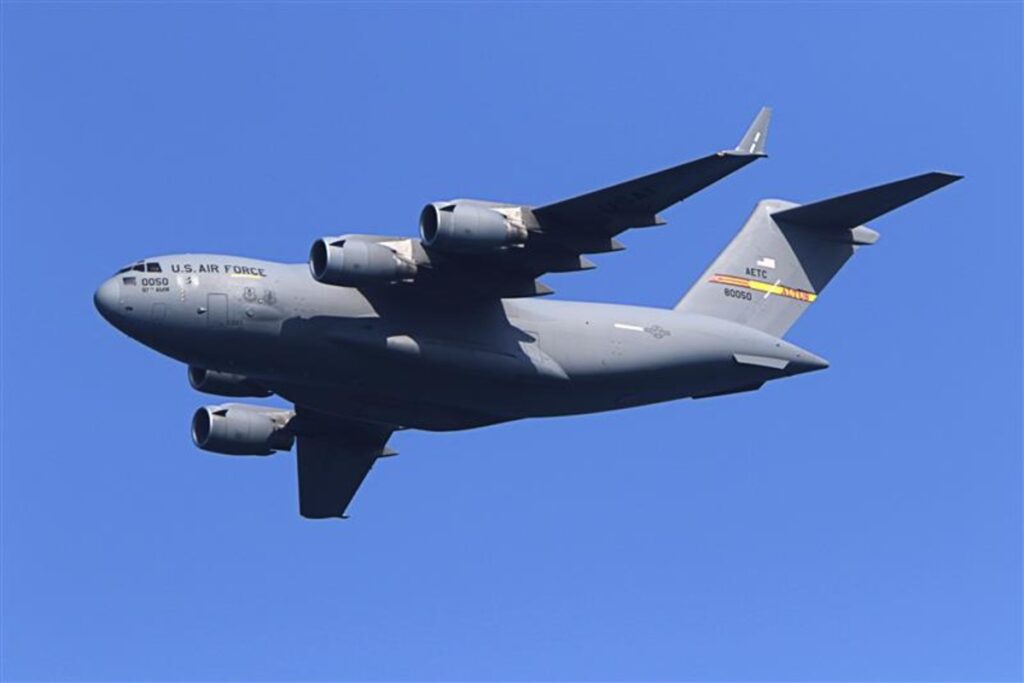
Flight tracking data shows that a USAF C-17 cargo plane departed from Albuquerque for a flight of just over 10 hours to Lakenheath on July 16 and left the U.K. two days later.
“It looks like it went to England, dropped off those weapons and then it went back to regular operations in the U.S.,” William Alberque, a former head of NATO’s nuclear non-proliferation center, told Britain’s The Times.
The U.K. government announced last month it would buy at least 12 F-35A fifth-generation aircraft, which, unlike the F-35B jets the country’s RAF already operates, are certified to carry nuclear weapons. The jets will be stationed at RAF Marham, a base north of Lakenheath.
The purchase “reintroduces a nuclear role for the Royal Air Force for the first time since the UK retired its sovereign air-launched nuclear weapons following the end of the Cold War,” the British government said in a statement.
The U.K. has Trident, its own nuclear weapons program made up of four Vanguard-class submarines able to fire nuclear missiles.
The U.S. has both strategic and nonstrategic nuclear weapons. Nonstrategic nuclear weapons, which in the U.S. case are variants of the B61 gravity bomb, are also known as tactical nuclear weapons. The U.S. announced at the start of the year that it had completed a long-running program to upgrade the B61 to the B61-12.
Strategic nuclear weapons are deployed on intercontinental ballistic missiles, submarine-launched ballistic missiles, and those fired from bomber aircraft. They are thought of as the missiles that could level entire cities and threaten major global superpowers.
Unlike strategic weapons, tactical nuclear weapons are designed for use on the battlefield or in what is known as a specific theater. They have a smaller yield and are designed to be used against different targets than strategic nuclear weapons, which are limited under the New START Treaty that is due to expire in 2026.
The U.S. has an estimated 200 tactical nuclear weapons, with roughly half deployed at European bases. The U.S. is believed to have around 100 tactical bombs deployed in five NATO countries on the continent, including in Turkey, Germany and Belgium.
What People Are Saying
Sidharth Kaushal, a senior research fellow with the British think tank, the Royal United Services Institute, told The Times that the C-17 flight “could be the transport of B61s for potential use on RAF F-35As in due course.
Kaushal added, “It represents a move towards the use of tactical nuclear weapons. It reintroduces a bit of flexibility in terms of how nuclear weapons are used.”
Read the full article here